|
|
Last edited by hbghlyj 2023-8-14 12:54Mathematical Analysis, Apostol著, 213页, Exercise 8.26|
Determine all real values of $x$ for which the following series converges:
$$\sum_{i=1}^∞\left(1+\frac12+\dots+\frac1n\right)\frac{\sin nx}n.$$ |
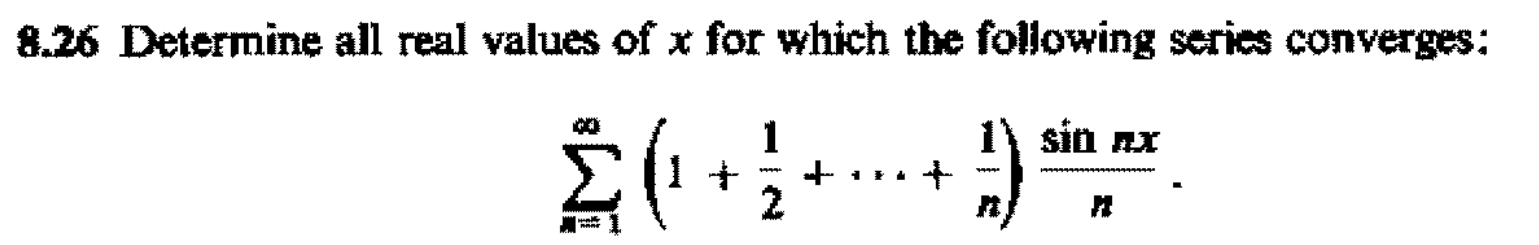
|
If $\sin\frac x2 = 0,$ then the sum is obviously zero. So assume otherwise.
Then, show two things:
- $b_n = \sin x+\sin(2x)+...+\sin(nx)$ is uniformly bounded over all $n$ for given $x$ by Theorem 8.30.
- $a_n = \frac 1n\left(1+\frac 12 +\frac 13+\dots + \frac 1n\right)$ is monotonically decreasing to zero.
(MSE)Proof: Use the fact that $x↦\frac1x$ is decreasing over $[1,∞)$ to get
$$
0<1+\frac12+\frac13+\cdots+\frac1n<1+\int_1^n\frac{dx}x=1+\log n
$$giving
$$
0<\frac1n\left(1+\frac12+\frac13+\cdots+\frac1n\right)<\frac1n+\frac{\log n}n.
$$
Then, you will be ready to use Theorem 8.28 (Dirichlet Criterion). |
|