|
|
original poster
hbghlyj
posted 2024-3-4 05:35
经过一些坐标变换,可以在3维画出来,例如:
https://mathworld.wolfram.com/CayleyCubic.html
If the ordinary double points in projective 3-space are taken as (1, 0, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 0, 1), then the equation of the surface in projective coordinates is
\begin{equation} {1\over x_0}+{1\over x_1}+{1\over x_2}+{1\over x_3}=0 \end{equation}
(Hunt). Defining coordinates with plane at infinity $v=x_0+x_1+x_2+2x_3$ and
\begin{align}x={x_0\over v}\\y= {x_1\over v}\\z= {x_2\over v}\end{align}
then gives the equation
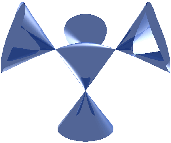
\begin{equation} -5(x^2y+x^2z+y^2x+y^2z+z^2y+z^2x)+2(xy+xz+yz)=0 \label5\end{equation}
plotted in the left figure above (Hunt). The slightly different form
\begin{equation} 4(x^3+y^3+z^3+w^3)-(x+y+z+w)^3=0 \end{equation}
is given by Endraß which, when rewritten in tetrahedral coordinates, becomes
\begin{equation} x^2+y^2-x^2z+y^2z+z^2-1=0, \label7\end{equation}
plotted in the right figure above.

|
| | \eqref{5} | \eqref{7} |
The Hessian of the Cayley cubic is given by WolframAlpha
\begin{equation}
\begin{split}
0&={x_0}^2(x_1x_2+x_1x_3+x_2x_3)+x_1^2(x_0x_2+x_0x_3+x_2x_3)\\
&\quad+x_2^2(x_0x_1+x_0x_3+x_1x_3)+x_3^2(x_0x_1+x_0x_2+x_1x_2).
\end{split}
\end{equation}
in homogeneous coordinates $x_0$, $x_1$, $x_2$, and $x_3$.
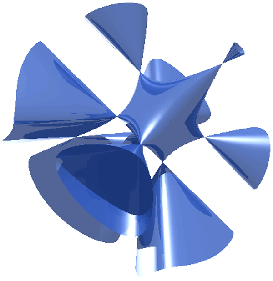
Taking the plane at infinity as $v=5(x_0+x_1+x_2+2x_3)/2$ and setting $x$, $y$, and $z$ as above gives the equation
\begin{equation}
\begin{split}
25&[x^3(y+z)+y^3(x+z)+z^3(x+y)]+50(x^2y^2+x^2z^2+y^2z^2)
\\&-125(x^2yz+y^2xz+z^2xy)+60xyz-4(xy+xz+yz)=0,
\end{split}\label9
\end{equation}
plotted above (Hunt). The Hessian of the Cayley cubic has 14 ordinary double points, four more than a the general Hessian of a smooth cubic surface (Hunt).
| | \eqref{9} |
|
|