|
|
Last edited by hbghlyj 2022-8-7 22:58pi.math.cornell.edu/~boyang/2220 s2017/math22 … es/notes_sec_2.1.pdf
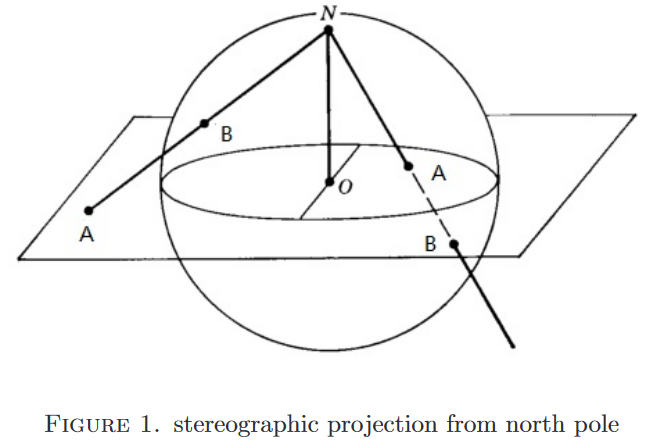
$S: \mathbb{R}^{2} \rightarrow S \backslash\{N\}$ has the formula: $$ S(x, y)=(X, Y, Z)=\left(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+y^{2}+1}, \frac{2 y}{x^{2}+y^{2}+1}, \frac{x^{2}+y^{2}-1}{x^{2}+y^{2}+1}\right) $$
| It is not hard to show that $S$ has an inverse function $F: S \backslash\{N\} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{2}$ : $$ F(X, Y, Z)=(x, y)=\left(\frac{X}{1-Z}, \frac{Y}{1-Z}\right) \text {. } $$ |
|
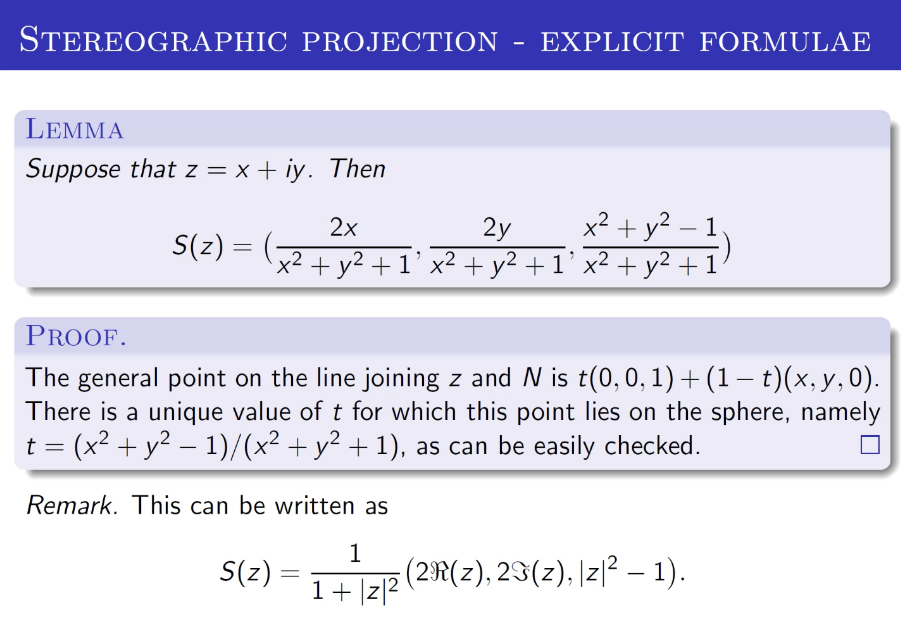
| PROOF.
The general point on the line joining $z$ and $N$ is $t(0,0,1)+(1-t)(x, y, 0)$. There is a unique value of $t$ for which this point lies on the sphere, namely $t=\left(x^{2}+y^{2}-1\right) /\left(x^{2}+y^{2}+1\right)$, as can be easily checked.
Remark This can be written as$$S(z)=\frac{1}{1+|z|^{2}}\left(2 \Re(z), 2 \Im(z),|z|^{2}-1\right)$$
|
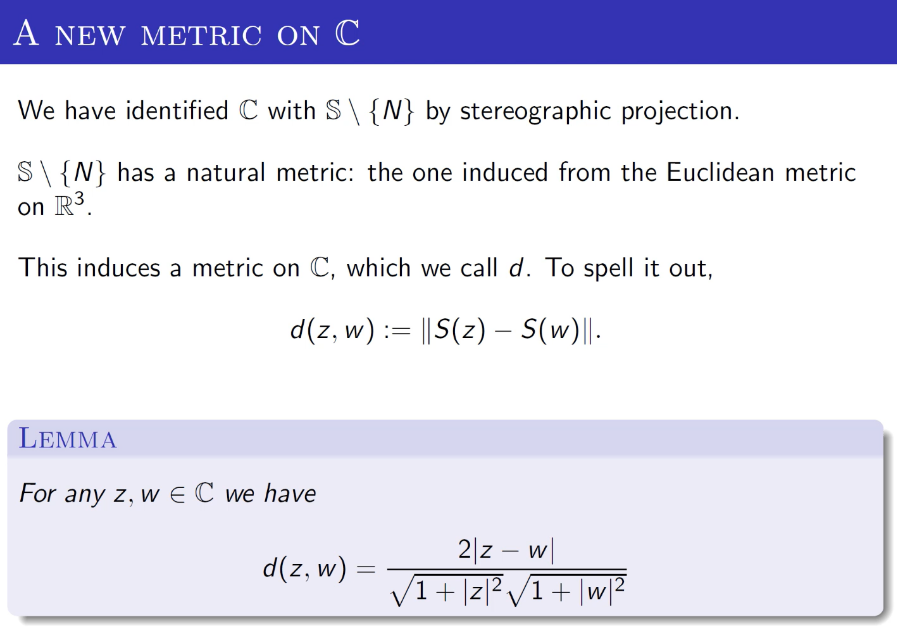
| We have identified $\mathbb{C}$ with $\mathbb{S} \backslash\{N\}$ by stereographic projection. $\mathbb{S} \backslash\{N\}$ has a natural metric: the one induced from the Euclidean metric on $\mathbb{R}^{3}$. This induces a metric on $\mathbb{C}$, which we call $d$. To spell it out, $$ d(z, w):=\|S(z)-S(w)\| . $$ LEMMA
For any $z, w \in \mathbb{C}$ we have $$ d(z, w)=\frac{2|z-w|}{\sqrt{1+|z|^{2}} \sqrt{1+|w|^{2}}} $$
|
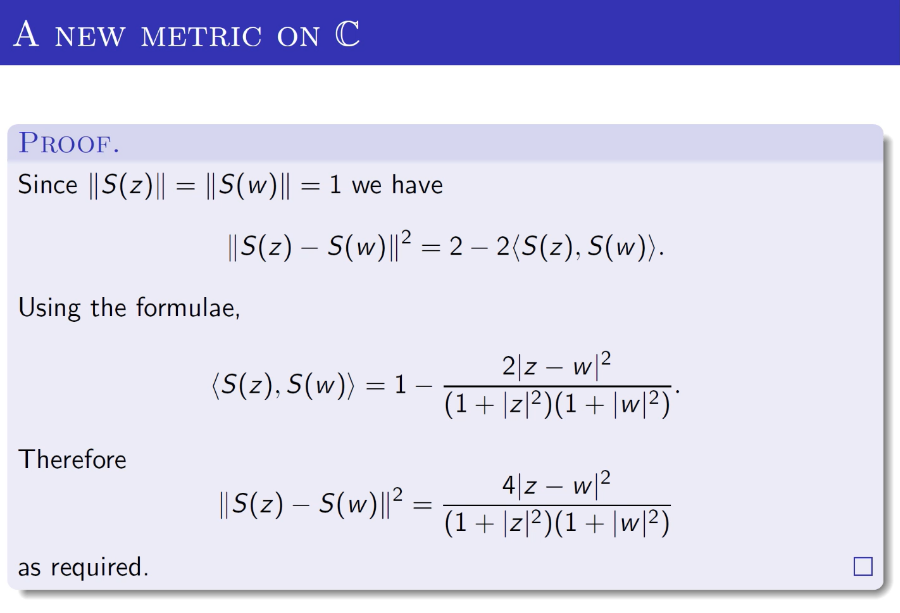
| Since $\|S(z)\|=\|S(w)\|=1$ we have $$ \|S(z)-S(w)\|^{2}=2-2\langle S(z), S(w)\rangle . $$ Using the formulae, $$ \langle S(z), S(w)\rangle=1-\frac{2|z-w|^{2}}{\left(1+|z|^{2}\right)\left(1+|w|^{2}\right)} . $$ Therefore $$ \|S(z)-S(w)\|^{2}=\frac{4|z-w|^{2}}{\left(1+|z|^{2}\right)\left(1+|w|^{2}\right)} $$ as required. |
|
|